|
|
|


Radio
program formats differ by country, regulation and markets. For
instance, the U.S. Federal Communications Commission designates the
88–92 megahertz band in the U.S. for non-profit or educational
programming, with advertising prohibited. |

See
Shortwave for the differences between shortwave, medium wave and long
wave spectra. Used largely for international broadcasts by organs of
state propaganda, religious organizations, militaries and others. |

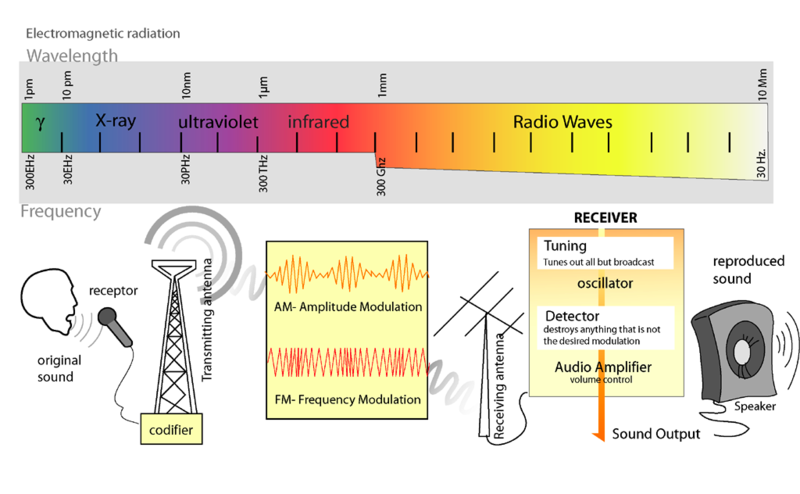
Radio
broadcasting is an audio (sound) broadcasting service, broadcast
through the air as radio waves (a form of electromagnetic radiation)
from a transmitter to an antenna and a thus to a receiving device.
Stations can be linked in radio networks to broadcast common
programming, either in syndication or simulcast or both. Audio
broadcasting also can be done via cable FM, local wire networks,
satellite and the Internet. |

AM
stations were the earliest broadcasting stations to be developed. AM
refers to amplitude modulation, a mode of broadcasting radio waves by
varying the amplitude of the carrier signal in response to the
amplitude of the signal to be transmitted. |

FM
refers to frequency modulation, and occurs on VHF airwaves in the
frequency range of 88 to 108 MHz everywhere (except Japan and Russia).
Japan uses the 76 to 90 MHz band. Russia has two bands widely used by
the Soviet Union, 65.9 to 74 MHz and 87.5 to 108 MHz worldwide
standard. FM stations are much more popular in economically developed
regions, such as Europe and the United States, especially since higher
sound fidelity and stereo broadcasting became common in this format. |

Many
countries outside of the U.S. use a similar frequency band for AM
transmissions. Europe also uses the long wave band. In response to the
growing popularity of FM radio stereo radio stations in the late 1980s
and early 1990s, some North American stations began broadcasting in AM
stereo, though this never gained popularity, and very few receivers
were ever sold. |

Although
now being eclipsed by internet-distributed radio, there are many
stations that broadcast on shortwave bands using AM technology that can
be received over thousands of miles (especially at night). For example,
the BBC has a full schedule transmitted via shortwave. These broadcasts
are very sensitive to atmospheric conditions and solar activity. |

The
best known type of radiostation are the ones that broadcast via
radiowaves. These include foremost AM and FM stations. There are
several subtypes, namely commercial, public and nonprofit varieties as
well as student-run campus radio stations and hospital radio stations
can be found throughout the developed world. |

Also,
many other non-broadcast types of radio stations exist. These include
base stations for police, fire and ambulance networks, military base
stations, dispatch base stations for taxis, trucks, and couriers,
emergency broadcast systems, and amateur radio stations. |

Satellite
radiobroadcasters are slowly emerging, but the enormous entry costs of
space-based satellite transmitters, and restrictions on available radio
spectrum licenses has restricted growth of this market. In the USA and
Canada, just two services, XM Satellite Radio and Sirius Satellite
Radio exist. Both XM and Sirius are owned by Sirius XM Radio, which was
formed by the merger of XM and Sirius on July 29, 2008, whereas in
Canada, XM Radio Canada and Sirius Canada remain separate companies. |