|
|
|

 |
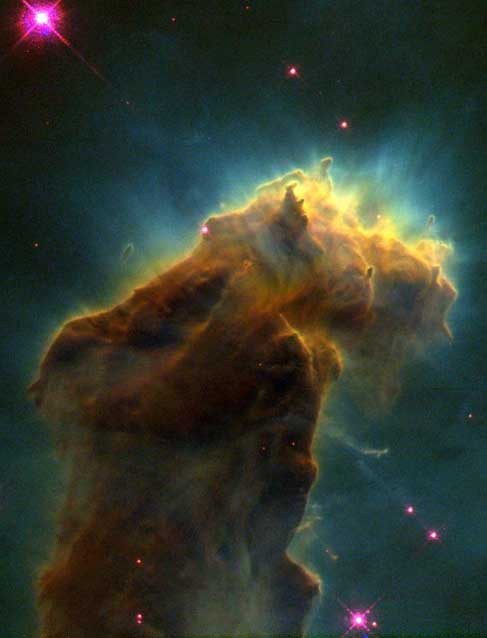
| Where do stars form? One place, star forming regions known as "EGGs", are uncovered at the end of this giant pillar of gas and dust in the Eagle Nebula (M16). EGGs, short for evaporating gaseous globules, are dense regions of mostly molecular hydrogen gas that fragment and gravitationally collapse to form stars. Light from the hottest and brightest of these new stars heats the end of the pillar and causes further evaporation of gas - revealing yet more EGGs and more young stars. This picture was taken by the Wide Field and Planetary Camera on board the Hubble Space Telescope. |
|
CURRENT
MOON
|
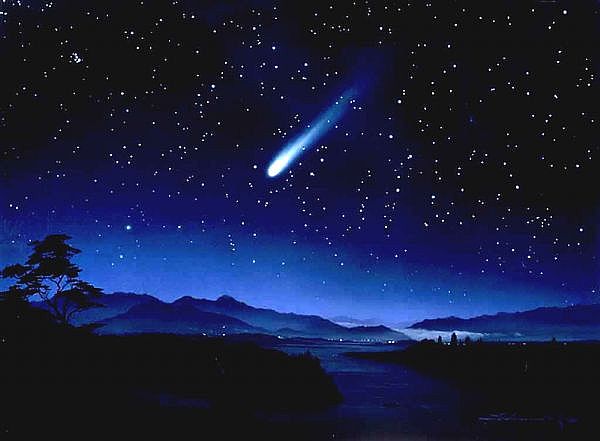 |
| Comets are cosmic icebergs. They follow very elongated orbits which carry them from the frozen, remote outer reaches of the Solar System to close encounters with the Sun. Heated by sunlight, they slough off layers of material as gas and dust, forming their characteristic awe-inspiring comas (heads) and tails. |
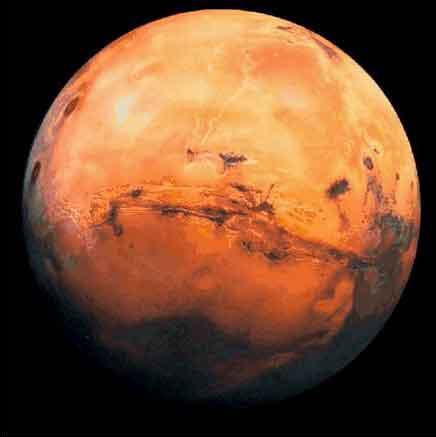 |
| For centuries, astronomers have observed Mars, patiently compiling many facts and theories. Like a distant mirror of Earth dwellers' hopes and fears for the future, Mars, the fourth planet from the sun, has inspired profound works of fiction as well. Classics of the science fiction genre with visions of Earth's alluring planetary neighbor include H.G. Wells' terrifying "War of the Worlds", Edgar Rice Buroughs' John Carter adventure series (Thuvia, Maid of Mars, The Gods of Mars, A Princess of Mars, The Warlord of Mars), Robert Heinlein's youthful "Podkayne of Mars", and Ray Bradbury's reflective and philosophical "The Martian Chronicles". Through the years scientific theories about Mars have been disproven, but the sense of wonder and adventure embodied in these works of fiction remain with us. |
 |
| Is
life imitating art? If you watched either of the 1998 movies Deep
Impact or Armageddon, you may have an idea of the future that faces
Earth. Or not. On July 9, 2002, the Lincoln Near Earth Asteroid Research Project (an MIT Lincoln Laboratory program funded by the United States Air Force and NASA) in New Mexico detected a 1.2-mile-wide (2 km) asteroid. It has an orbit around our sun of 837 days, and early calculations indicate there is a small chance that this asteroid will collide with Earth on February 1, 2019. |
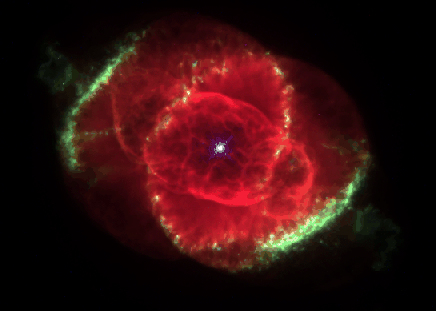
| Three thousand light-years away, a dying star throws off shells of glowing gas. This image from the Hubble Space Telescope reveals the Cat's Eye Nebula to be one of the most complex planetary nebulae known. In fact, the features seen in the Cat's Eye are so complex that astronomers suspect the bright central object may actually be a binary star system. The term planetary nebula, used to describe this general class of objects, is misleading. Although these objects may appear round and planet-like in small telescopes, high resolution images reveal them to be stars surrounded by cocoons of gas blown off in the late stages of stellar evolution. | |